Weather Fundamentals
Composition of the Atmosphere
Layers:
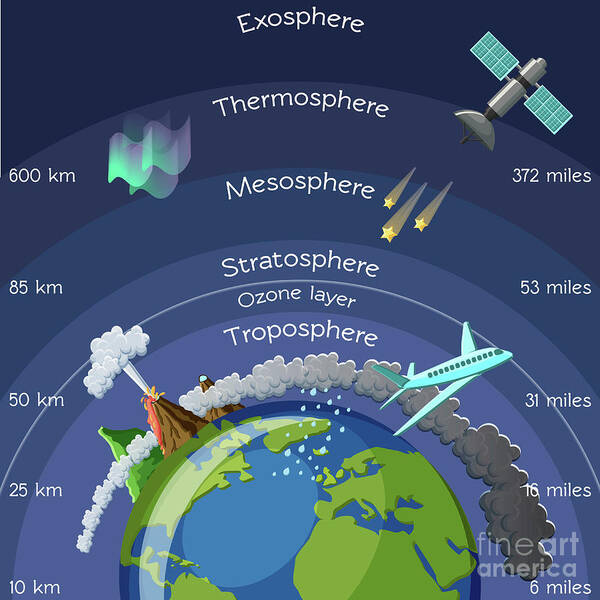 Thermopause
Thermosphere
Mesophere
Stratosphere
Ozone layer
Troposphere
Thermopause
Thermosphere
Mesophere
Stratosphere
Ozone layer
Troposphere
Weather happens in the Troposphere
Atmosphering Circulation
Cause of all weather is uneven heating of the earth's surface
Coriolis Force
Wind caused by earth's rotation
Atmospheric Pressure
Sea level 14.7ls
Every 1000ft, pressure drops about an inch of mercury
Aneroid wafers
Winds and Currents
The air over the sea heats up more slowly than over land.
High pressure - usually brings better weather Move clockwise outwards and downwards (COD) COD
Low pressure - brings worse weather counter clockwise, inwards, upwards??
Bom cyclones
To get a tailwind You want to be south of a low pressure, north of a high pressure
Effects of Obstructions on Winds
Obstructions can cause downdrafts
Mountain Winds
Cross mountains at a 45degree angle - makes it so you can turn around without having to turn as much (90 egrees instead of 180)
Winds above 20kts gets ...scary??
Windshear
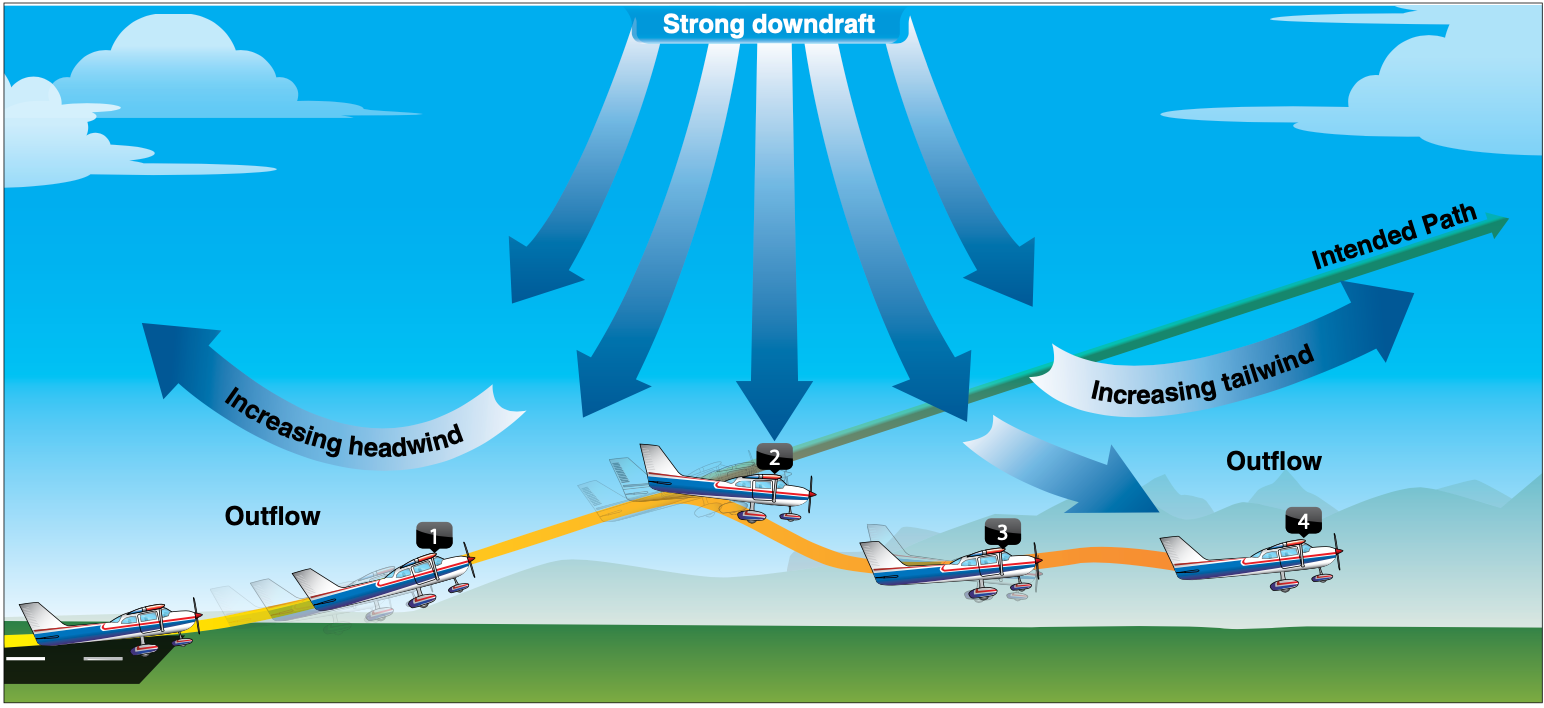
Spot #1 you get an increase in performance
If you had a headwind and then
Don't fly if there's any windshear.
Fly a landing approach faster in wind shear
Atmospheric Stability
The atmosphere's ability to resist vertical lift
Adiabatic Heating and Cooling
2 degrees / 5.4 F temperature drop per every 1000 ft of altitude
Moisture and Humidity
Relative Humidity
RH represents the amount of water in air in percentage
Gives us insight into if cloud are going to form
Dew point
At 100% humidity, there will be some sort of visible moisture
Temerature Inversions
When you go up in altitude and it gets warmer instead of cooler
Cloud Characteristics
Stratus clouds: Low level, stable clouds Stratocumulous
Towering cululus or cumulonimbus are tall and have a lot of
Stratiform Clouds: The blanket clouds that stretch a ways
Cumulus clouds are fluffy
Air Masses
Cold fronts
Usually bring worse weather and move faster
All fronts bring wind changes and temperature changes
Warm Front
Occluded Front
When a cold from overtakes a warm front and everything mixes together
Thunderstorms
Three stages
- Cumulus
- Mature
- Dissipating
- Most dangerous because of down drafts
3 ingredients
- moisture
- unstable air
- lifting force
If there is a thunderstorm, you're supposed to stay 50-60 nm away. They can throw hail really, really far. (About 15m?)
Characterized by the anvil top shape
Water molecule is sent up. When it goes up, it becomes ice. The ice falls, hits the water molecules. When it hits, it creates static electricity.
Icing
Three types
Clear icing: rain hits aircraft and then freezes Rime: Freezes right away. Causes the most drag and decreases lift Mixed
Want to land if you start to get icing
Fog
Radiation Fog
Think zombies on farm fog
Forms on clear nights with low temp and dew point spread is low/small
Overnight, air cools to it's dew point, condenses and creates fog
Advection Fog
Cold air mass moving over a warm air mass, fog happens from the cooling "Marine layer"
Steam fog
Air that moves over a warm body of water, heats up, forms steam. Less common
Upslope Fog
Air mass is forced up a hill, cooled to it's dew point
Precipitation fog
Extra fine, small rain particles
Freezing fog
Less common around here.
Air particles frozen and suspended in the air
Need to know -
Microbursts Advection and radiation fogs Thunderstorms Vergo clouds - indication that there's a microburst
IMSAFE I Medication Stress Alchohol Fatigue E
Quiz
1. Decode this METAR:
KHIO 131653Z 13005KT 6SM -RA BR OVC033 04/04 A2979 RMK AO2 SLP090 P0003 T00440039
Hillsboro
13th at 8:53am
Wind 130 @ 05kts
6SM visibility
Light rain
Mist
Overcast 3300
Temperature 4°C
Dewpoint 4°C
Altimeter 29.79
2. What is a PIREP? Are there different kinds? What are they for?
A pilot report
There can be urgent or normal PIREPs
They are often for cloud cover, icing, turbulence, wind shear, etc.
3. Decode this TAF:
KHIO 131137Z 1312/1412 14004KT 4SM BR OVC005
FM131800 14008KT 5SM -RA SCT010 OVC025
FM132100 13008KT 2SM -RA BR BKN007 OVC015
FM140500 15010KT 4SM -RA BR OVC015
Hillsboro
13th at 3:37am from the 13th at 12 to the 14th at 12
Winds 140 @ 04kts 4SM visibility mist overcast 500
From 13th at 10am winds 140 @ 08kts 5SM visibility light rain scattered 1000 overcast 2500
From 13th at 1pm winds 130 @ 08kts 2SM visibility light rain mist broken 700 overcast 1500
From 13th at 9pm winds 150 @ 10kts 4SM visibility light rain mist overcast 1500
4. What are the 3 kinds of AIRMETS?
Tango - Turbulence
Sierra - Mountain Obscuration or IFR
Zulu - Icing
5. What are examples of some SIGMETS? How long is a convective SIGMET valid for?
Tango, Sierra, Zulu, and a convective SIGMET is valid for 2 hours.
Tornadoes, thunderstorms are examples.
6. What is Hypoxia vs Hyperventilation?
Hypoxia is not enough oxygen in the body
Hyperventilation is too much CO2
7. How long should you wait after drinking to fly?
8 hours bottle to throttle, 0.04 blood alcohol
Details
8. What does IMSAFE stand for?
IllnessMedication
Stress
Alcohol
Fatigue
Emotion
9. What are the 5 hazardous attitudes?
Macho: "I can do it!" Anti-Authority: "Don't tell me what to do!" Impulsivity: "Do something quickly!" Invulnerability: "It won't happen to me!" Resignation: "What's the use?"